Research
Minimising Task Tardiness for Multi-Agent Pickup and Delivery
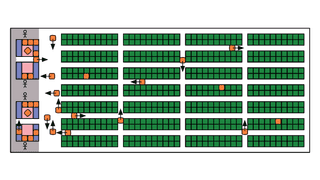
Multi-agent pickup and delivery,a variant of the multi-agent path finding problem, aims to find collision-free paths for a set of agents performing a continuous stream of pickup and delivery tasks. Owing to the service guarantee nature of applications, these agents of ten need to execute the tasks within their stipulated deadlines. When failure to meet task deadlines is unavoidable, there is a need to minimise the tardiness experienced by the tasks. To address this problem, we propose a cost-ba ...
Multi-Agent Path Execution with Uncertainty
In real-world multi-agent applications, unexpected conditions can break the assumptions made in path planning and degrade the effectiveness of path execution. This paper studies robust and effective execution of multi-agent path plans under uncertainty. To guarantee conflict-freeness and deadlock-freeness, we define a feasibility problem to check whether the remaining portion of a path plan can be successfully executed. We prove that the problem is NP-complete and propose a feasibility test algo ...
Multi-Agent Pickup and Delivery with Individual Deadlines
We study the multi-agent pickup and delivery problem with task deadlines, where a team of agents execute a batch of tasks with individual deadlines to maximize the number of tasks completed by their deadlines. Existing approaches to multi-agent pickup and delivery typically address task assignment and path planning separately. We take an integrated approach that assigns and plans one task at a time taking into account the agent states resulting from all the previous task assignments and path pla ...
Playground: A Safe Building Operating
Building operating systems are an emerging class of system software that provides services to applications running on commercial buildings. The current state-of-the-art requires applications to be trusted and carefully monitored due to a lack of authorization, access control, and execution isolation mechanisms in existing building operating systems. Proposed solutions do not adequately handle the complexity and scale of modern buildings, therefore impeding the adoption of applications that can e ...
Robust Continuous-Time Multi-Agent Path Execution
Most prior work on multi-agent path finding and execution has assumed that time is discretized into timesteps and the agents move in grid maps with uniform action durations. However, in real-world multi-agent applications, agents of different shapes can move in arbitrary directions, and unforeseen failures and anomalies can cause unexpected delays of the agents. These delays are difficult to model and predict, and they can break the assumptions made in path planning and degrade the effectiveness ...